China’s GDP growth surprises the market once again in 2017
Source:marketrealist
China’s (MCHI) economy surprised the markets when it rose 6.9% year-over-year (or YoY) in 2017.
China’s economy
China’s (MCHI) economy surprised the markets when it rose 6.9% year-over-year (or YoY) in 2017. This rise was the economy’s biggest in the last six consecutive quarters, and it was driven by fiscal and monetary stimulus. Increased investment in infrastructure development and real estate also boosted the country’s economic growth in 2017.
China (YINN) is currently in a transitional phase as it moves from being an export-based economy to a consumption-based economy. Let’s look at China’s GDP growth in the last year as of July 17, 2017.
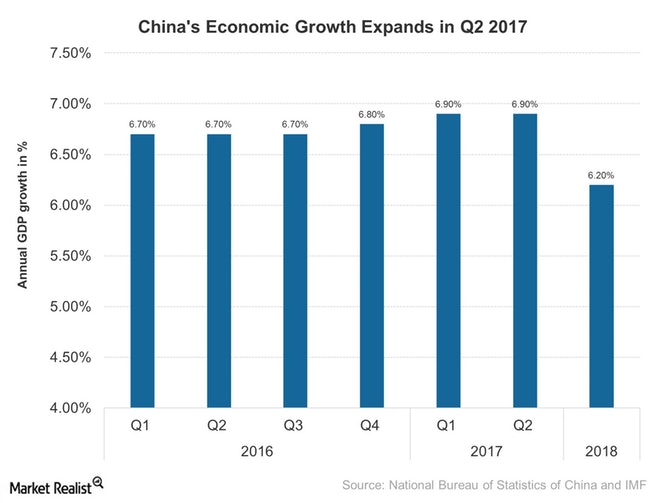
Economic growth in 2017
China’s 2017 economic growth exceeded the market’s expectation of a 6.8% expansion. The country’s 2017 growth rose sharply compared to 3015, mainly due to increased industrial output, higher retail sales, and stronger fixed-asset investments.
Industrial production in 2017
Chinese industrial production rose 7.6% YoY in 2017, compared to 6.5% in the previous quarter. The country’s industrial output exceeded the market’s expectation of a 6.5% rise in 2017. It recorded this steep rise for the following reasons:
Manufacturing rose 8%, compared to 6.9% in the previous month.
Electricity, gas, and water production rose 7.3%, compared to 6.4% in the previous month.
Mining fell 0.1%, compared to a 0.5% fall in the previous month.
Improved demand situation
Retail sales (XRT) also rose 11% YoY in 2017, beating the market’s expectation of a 10.6% rise. The country’s retail sales recorded the sharpest rise compared to December 2015, mainly due to higher sales in its telecommunications sector. Sales also rose in the automobile, building materials, furniture, office supplies, and personal care sectors.
Increased government spending
Chinese government spending rose 15.8% in 2017, compared to the same period last year. The country’s fiscal expenditure rose 19.1% YoY, compared to its 9.2% rise in May 2017.
Expectations
The Chinese government expects its GDP growth to be ~6.5% in 2017, still slightly below its GDP growth of 6.7% in 2016. This reduction in expectations comes from policy tightening and other reforms undertaken by Chinese officials to control rising debt levels and to get tough on the housing bubble. However, the high cost of debt is expected to affect consumption levels in China.
China’s economic growth in 1H17 provides encouraging data proving its progress in the transition to a consumer-based economic model. This strong economic growth is also reflected in China’s benchmark Shanghai Composite Index, which has risen ~1% month-to-date as of July 20, 2017.
The addition of 222 Chinese A large-cap stocks in the emerging market index improved the market sentiment in June 2017. The government also announced that it would increase its efforts to reform inefficient state companies, which improved performance across all sectors on July 19, 2017.
ETF performance
The iShares China Large-Cap ETF (FXI) and the SPDR S&P China ETF (GXC) had risen ~6% and 7%, respectively, in July 2017, as of July 20, 2017. These ETFs track the Chinese companies listed on the Hong Kong, China Stock Exchange.
(Source: marketrealist.com)
-

"2021 China Internet Home Improvement Consumption Trend White Paper" released
-

Sales of soft furniture such as sofas and beds in China doubled in August
-

China' s furniture retail sales in August was 13.7 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 6.7%
-

From January to August, China' s furniture exports reached 305.43 billion yuan, an increase of 31%

 沪公网安备31010402003309号
沪公网安备31010402003309号



